Key Points
- Central repository of hard-to-find information for GE Profile PFCF1NFW French-style, Bottom Freezer Refrigerator
- Detailed specification and operational information on main components
- Links to detailed repair articles in the HOW-TO-ARTICLES section
Table of Contents
- Applicable Models
- Model Naming Convention
- Specifications
- How Does It Work
- Condenser Fan
- Thermistors
- Maintenance
- How-to Articles
- Reference Links
- Check for Possible Recalls
Applicable Models
GE Profile Refrigerator PCFC1NFW is a counter-depth French-door refrigerator with ice maker. It features easy to reach temperature controls in the front with “Turbo Cool” setting.
PFCF1NFW model series were manufactured from May 2007 through February 2008.
- PFCF1NFWWW – White
- PFCF1NFWBB – Black
- PFCF1NFWSS – Stainless Steel
- PFCS1NFW
- PFIC1NFW
You may also find the information may also be applicable to the following GE refrigerator models:
- PDCF1NBW
- PFCF1NFC
- PFCF1NFX
- PFCF1NFYA
- PFCF1NFZ
- PFCF1NJW
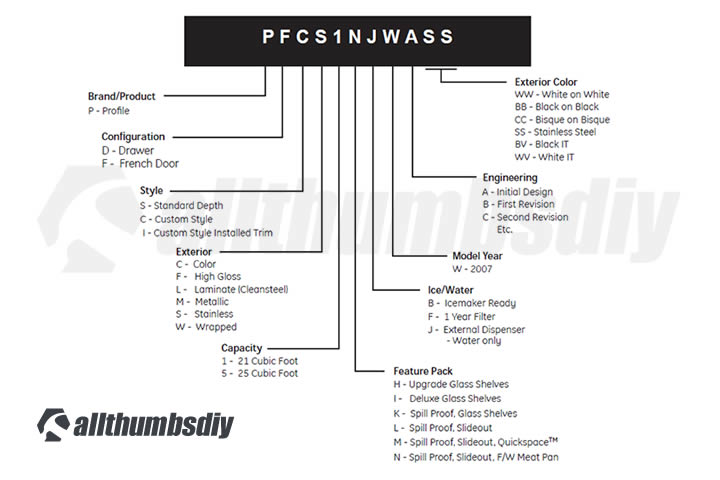
Model Naming Format
- Brand Product
- P = Profile
- Configuration
- D = Drawer
- F = French Door
- Style
- S = Standard Depth
- C = Custom Style
- I = Custom Style Installed Trim
- Exterior
- C = Color
- F = High Gloss
- L = Laminate (Cleansteel)
- M = Metallic
- S = Stainless
- W = Wrapped
- Capacity
- 1 = 21 cubic foot
- 5 = 25 cubic foot
- Feature Pack
- H = Upgrade Glass Shelves
- I = Deluxe Glass Shelves
- K = Spill Proof, Glass Shelves
- L = Spill Proof, Slideout
- M = Spill Proof, QuickSpace
- N = Spill Proof, Slideout, F/W Meat Pan
- Ice / Water
- B = Icemaker Ready
- F = 1-year Filter
- J = External Dispenser (water only)
- Model Year
- W = 2007
- Engineering
- A = Initial Design
- B = First Revision
- C = Second Revision, etc.
- Exterior Color
- WW = White on White
- BB = Black on Black
- CC = Bisque on Bisque
- SS = Stainless Steel
- BV = Black IT
- W = White IT
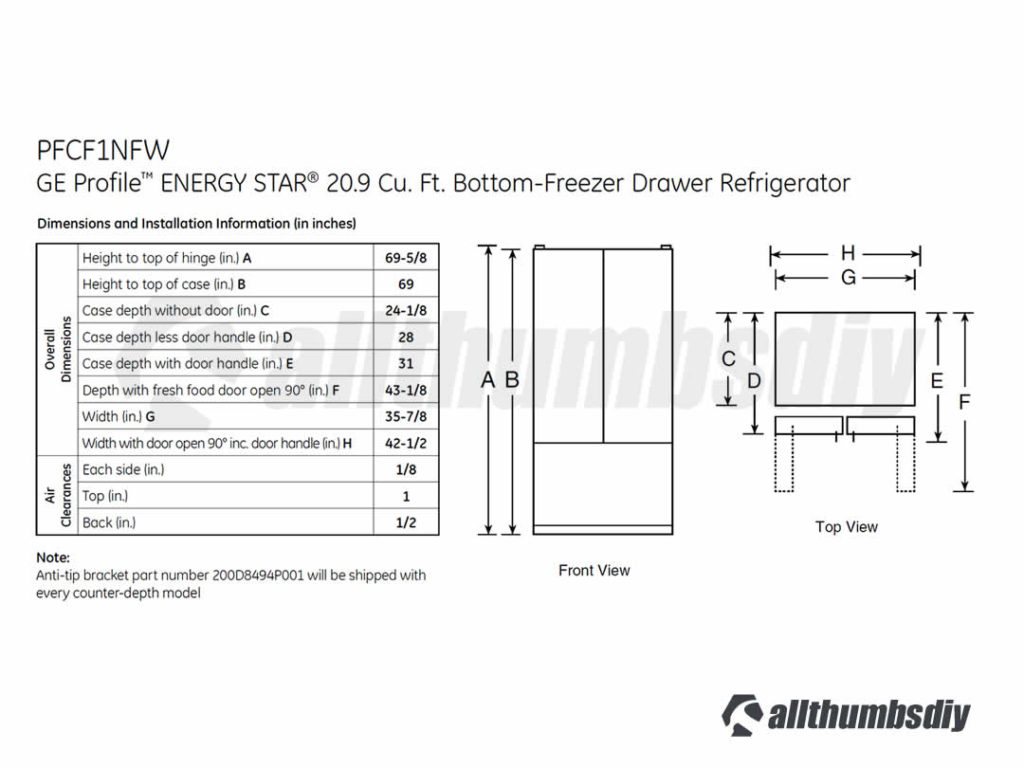
Specifications
| Appearance | High-Gloss White, Black or Stainless Steel |
| Door Stops | Yes |
| Door Swing | Hinges and Left and Right |
| Capacity, total | 20.9 cu ft |
| Capacity, fresh food | 14.6 cu ft |
| Capacity, frozen food | 6.3 cu ft |
| Temp. Management | 4 electronic sensors, multi-flow air tower, Turbo Cool |
| Defrost Type | Frost Guard |
| Door Alarm | Yes |
| Depth | 31.375 in |
| Height | 69.625 in |
| Width | 38.875 in |
| Power | 120v; 60 HZ, 15A |
Features
With the introduction of a new refrigeration platform in 2001, there were be many changes in features, benefits,
- Custom Cool™ Technology – Evaporator (freezer) fan would run without compressor/condenser fan running.
- Climate Keeper™ System – When either door was opened, the freezer and fresh food fans shut off. If the door is left open 3-minutes, the fan would come back on.
- Frostguard™ Technology – No air flow to the fresh food compartment when the evaporator fan (freezer fan) was on. Evaporator (freezer) fan, and the condenser/compressor fan could run up to 8-hours continuously.
- Turbo Cool™ setting – The evaporator (freezer) fan and the fresh food fan operated on 2-speeds which creates a different sound (both very quiet) with the evaporator (freezer) fan would run for 48 hours nonstop circulating cold air.
- Liner protection mode – Fresh food and freezer fan came on when the doors were opened for 3-minutes to protect the plastic from the heat coming off the lights.
- Adaptive defrost – Determined the need to defrost based on both door openings and compressor run time.
Liner Protection Mode
Liner Protection Mode (LPM) was created to prevent damage (primarily from the heat of the light bulbs) to the interior plastic liner of your refrigerator (interior plastic damage causes swap-outs of product returns, costing GE millions of dollars).
Because the Liner Protection Mode consists of several overriding functions , it can make your refrigerator behave in a way that masks the symptoms that are caused by totally unrelated components(s):
- After 3 minutes of freezer door not being closed
- The evaporator fan will turn on at high speed
- The damper to the fresh food compartment will close (make the compartment warm)
- `Th evaporator fan may run even during the defrost cycle (which will ironically warm up the freezer compartment)
DC Components in your refrigerator
Electrical energy is distributed as alternating current (AC) because AC voltage may be increased or decreased with a transformer.
This allows the power to be transmitted through power lines efficiently at high voltage, which reduces the energy lost as heat due to resistance of the wire, and transformed to a lower, safer, voltage for use.
However, electronics cannot run directly on AC as it requires rectified and filtered (smooth) DC power to supply the electronic circuitry within the device with a constant voltage. Many electronic circuits have several different DC voltages in the same device.
GE refrigerators have the following DC components:
- Evaporator fan motor: 4, 8 or 12 VDC depending on the fan tachometer/speed
- Condenser Motor: 12 VDC
- Thermistors: 5 VDC
- Damper motors: 2 VDC on standby; 6 VDC during operation
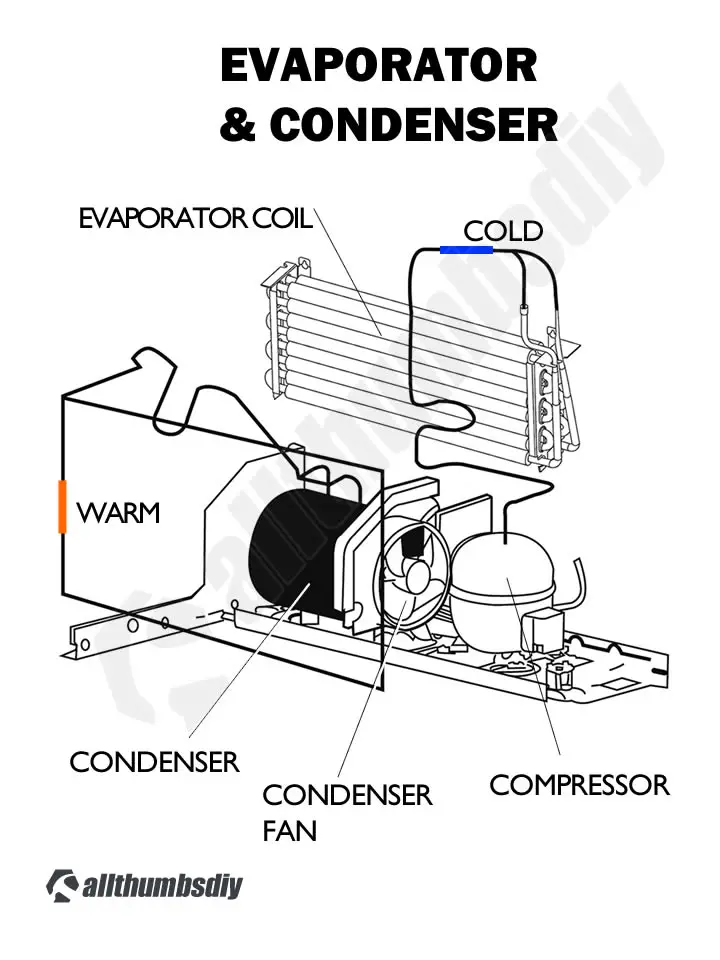
How Does GE Profile PFCF1NFW Refrigerator Work?
Although GE Profile refrigerators have some “cool” advanced features, the core refrigeration technology has not changed since it was originally invented back in the 1800’s: absorb heat by letting liquids into gases and release heat by compressing gases back into liquids via the evaporator and condenser.
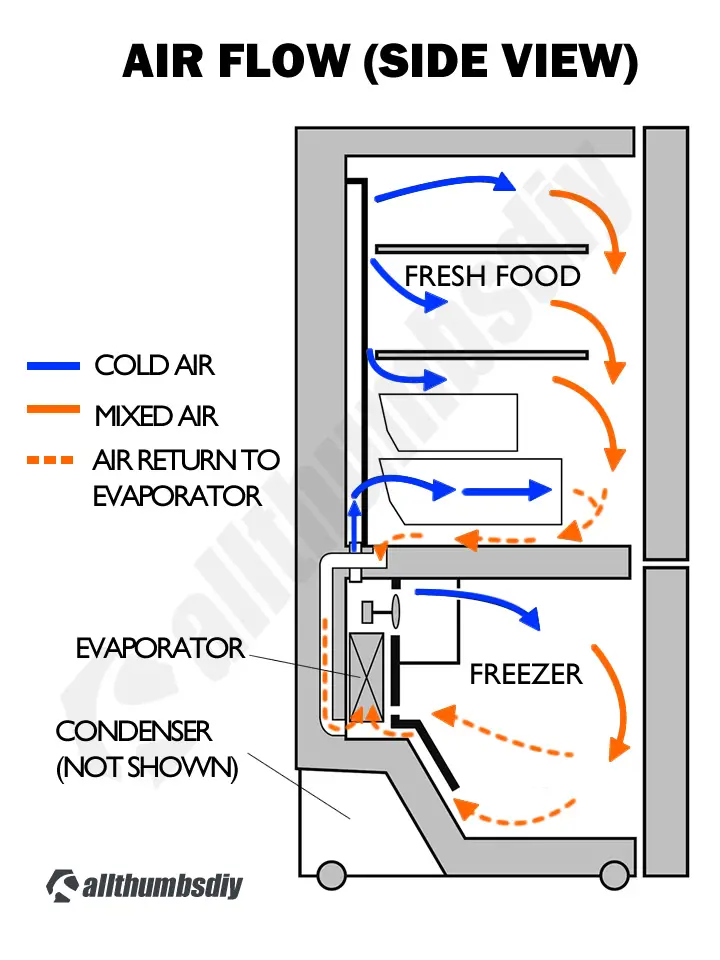
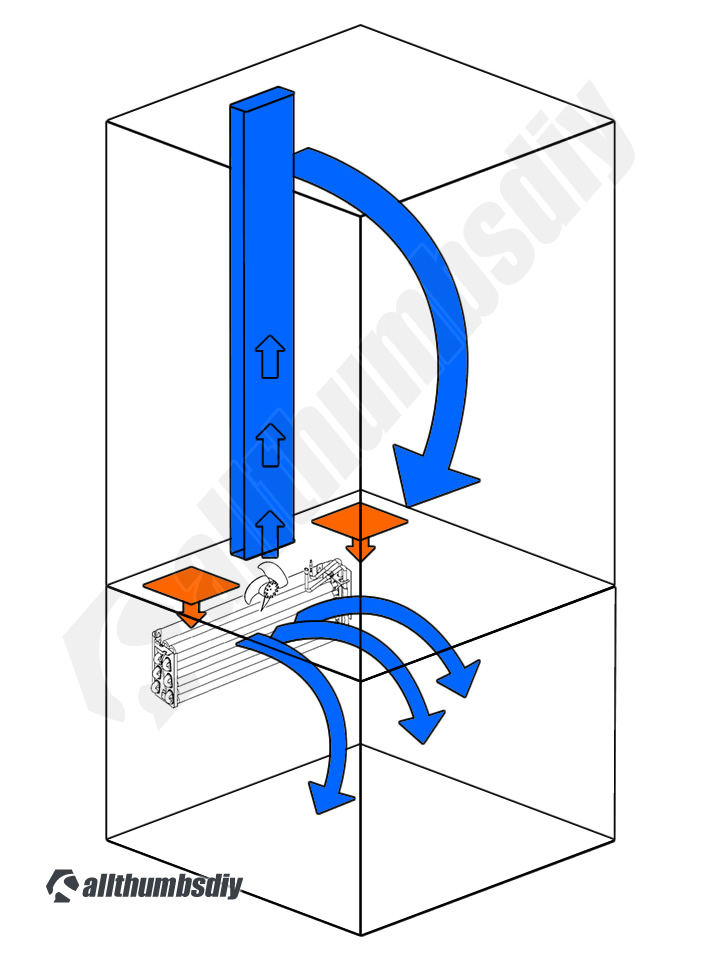
Unlike other models, GE Profile PFCF1NFW refrigerator uses a single evaporator fan to distribute cold air through out the fresh food (“FF”) and freezer (“FZ”) compartments.
Of course the fresh foods compartment temperature needs to be higher so PFCF1NFW uses an electronically controlled damper to control the amount of cold air into the FF compartment (warmer air is sent back to the freezer compartment via return ducts (highlighted in orange).
Compressor
Because the main component of a refrigerator is the compressor, highly durable and reliable compressor is a must.
So, all GE Profile refrigerators use a reciprocating compressor (a.k.a. Scotch Yoke compressor) which is designed to give years of reliable service.
Embraco reciprocating compressors consist of a single, reciprocating piston operating in a stationary cylinder:
- It is actuated through a sliding yoke by a crank on the upper end of a vertical shaft.
- The shaft is made of hardened steel and runs in cast iron bearings.
- The upper bearing is self-aligning, which helps eliminate wear.
- A rotary oil pump is at the bottom of the shaft, which keeps the compressor lubricated and operating smooth through years of use
Embraco compressors have three windings wit the same resistance. It is important to remember that the resistance across all three windings should not vary more than 1 ohm as that will prevent the compressor from working.
To learn how to properly test your compressor, read my post How to Troubleshoot a Refrigerator Compressor and Inverter article (TBD)
| GE Part Number Variations |
|---|
| When GE improves the original part, its part number changes as well. Please go to my parts page and lookup the diagram # to confirm the latest part number, price and availability. |
Inverter
The inverter board (a.k.a. speed control board or motor control unit) takes a three-phase voltage to run a refrigerator compressor.
In the old compressor/start relay setup, a compressor has a start and a main (a.k.a. run) windings and a start relay/capacitors. A start relay/capacitors are used to energize and start the motor, then a main winding takes over to keep the motor going using the standard 120 VAC.
In contrast, all modern refrigerators use an inverter+compressor combination to make refrigerators run more efficiently.
Unlike the old setup, the use of inverter allows compressors to work at variable speed so the refrigerator can slow down the compressor to maintain temperature and ramp up when a rapid cooling is desired.
An average DIYer (that’s me) do not have necessary equipment to test inverters so we have to resort to using process of elimination in deciding to replace the inverter or not.
To learn how to do such test, read my post How to Troubleshoot a Refrigerator Compressor and Inverter article (TBD)
Condenser Fan
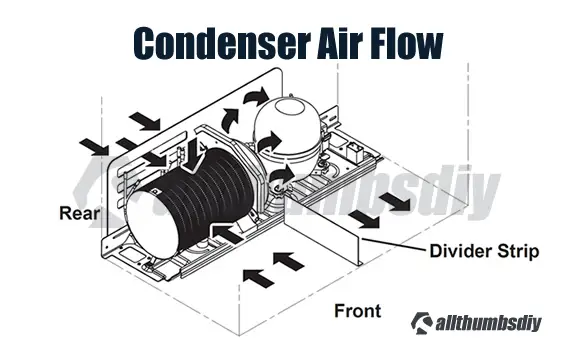
The fan is mounted in the rear machine compartment with what is supposed to be a no-clean condenser (unless you live in a surgical room clean environment, you WILL need to periodically clean this condenser with a condenser cleaning brush)
The fan and shroud are mounted on the left side of the condenser (next to the compressor assembly) and the other end is blocked with a rounded cardboard.
When the fan is operating, air is pulled from the outside into the center of the condenser (cooling the condenser coil during the process). The air is than directed over the compressor and out the right side of the refrigerator (cooling the compressor).
There are two passive, but very important components to this setup:
- rubber divider
- cardboard rear access cover
A rubber divider strip underneath the refrigerator divides the inlet and outlet sides of the machine compartment. Without this diver, hot air (comprised of heat from the condenser coil and compressor) can be recycled directly back into the condenser, creating a sub-optimal air flow.
The same concept applies to the rear cardboard access cover (Diagram # 616, Part # WR82X10109). It must be tightly fitted to prevent the air from being exhausted directly out of the rear of the machine compartment. This “leak” will bypass the compressor, resulting in the compressor being overheated.
Condenser Fan Speed
GE PFCF1NFW uses a variable speed fan for its condenser that corresponds with compressor speed (low, medium, high) to minimize pressure variations in the sealed system.
The only exception is when the freezer temperature is 20 F or above the set point (usually 0 F). If this condition is met (i.e. during initial startup), the condenser fan operates at super high speed while the compressor operates at medium speed.
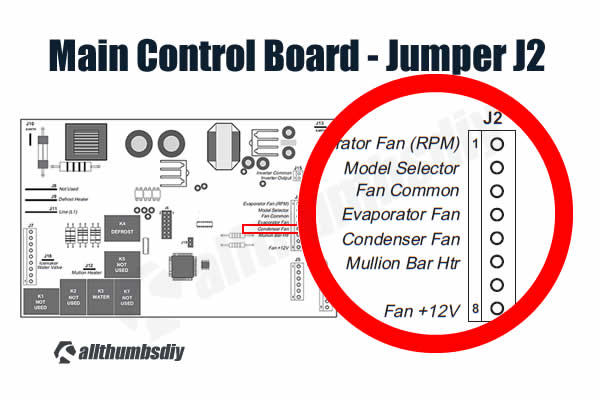
The speed of the fan is controlled by the voltage output from the main control board (Jumper J2).
The voltage output from the J2 jumper is 13.6 VDC via pulse width modulation (PWM), Fan speed is selected and maintained by the main control board, regulating the length and frequency of the 13.6 DVC pulse cycle.
Fan speed can vary + or – 5%, depending on the temperature, with higher temperatures causing slightly higher speeds.
Thermistors (Temperature Sensors)
Thermistor or temperature sensor is used to monitor fresh food and freezer temperatures. The sensor is a small capsule like device that is protected by a plastic shield and will vary in resistance depending on the temperature. The main control board uses this information to turn on the compressor and fan circuits as well as to operate the damper control.
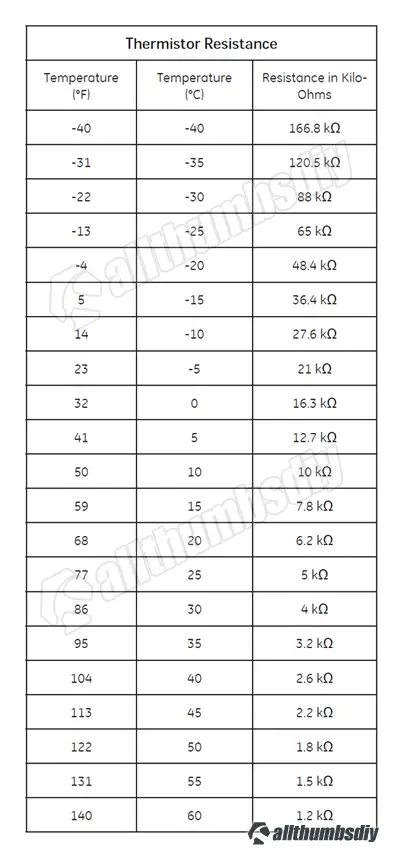
Thermistor – Resistance / Temperature Table
If a sensor becomes damaged or defective it may incorrectly signal the control board to turn off the compressor and fans and result in warmer than normal fresh food and freezer temperatures.
There are 4 thermistors to provide temperature data to the main control board:
- Fresh Food Thermistor
- Freezer Thermistor
- Ambient Thermistor
- Evaporator Thermistor
Fresh Food and Freezer Thermistors
The fresh food thermistor is located in the left wall of fridge compartment. The freezer thermistor is located in the right wall of the freezer compartment.
Ambient Thermistor
Ambient thermistor is attached to the front of the cabinet (under the left side of the freezer compartment) with a plastic wire tie, connected at J1-2 on the main control board.
When ambient temperature is below 60 F, the fresh food temperature control will shut down temporarily because the cooler room temperature assists in keeping fresh food temperatures at the preset temp. However, the compressor does not get enough run time to bring the freezer down to 0 F.
At higher room temperature data provided by the ambient thermistor, the main control board runs the compressor at higher speeds to get the freezer and fresh food compartments to an acceptable temperature.
It assists the main control board in compensating for room ambient that is higher or lower than 60 F.
Evaporator Thermistor
Evaporator Thermistor is clipped on to the suction tube line of the evaporator.
Evaporator Thermistor’s primary task is to monitor the temperatures of the evaporator coil and signal the board to terminate the defrost cycle when it senses the temperature between 60-70 F.
The main control board then terminates the power to the defrost relay.
Defrost Heater Temperature Sensor
The bi-metal thermostat located on the evaporator is used only as a backup safety measure to evaporator thermistor.
It is preset to open at 140 F and close at 110 F and will likely nevery activate unless the defrost resistors on the main control board somehow malfunctions.
When you are replacing the evaporator thermistor, I do recommend just replacing the defrost thermostat as well.
Damper Assembly
Damper is controlled by two motors to open and close the flap. It is either in an OPEN or CLOSED position (no partial opening).:
- 2 VDC – standby
- 6 VDC – operation
If the damper door is stuck in a partially open stage with voltage present, it will need to be replaced (go to my parts page to look up “Air Tower” assembly for the latest part number and availability)
Evaporator Fan
Evaporator fan is a DC motor and has four leads (with constant 12 VDC between red and white leads):
- Red: 12 volts to power the tachometer and PC board on motor
- White: common
- Blue: monitors fan speed for the board
- Yellow: active leads that supplies variable power from the main control board
- 4 VDC: low speed
- 8 VDC: medium speed
- 12 VDC: high speed
Reference Links
- Owner’s Support for PFCF1NFWBB, black on black model (link to GE support page)
- Owner’s Support for PFCF1NFWWW, white on white model (link to GE support page)
Energy Guide for PFCF1NFW

Quick Specs for PFCF1NFW
Installation Guide
The original link to GE support is broken. Please BobsManuals.com. If you still need help, please a comment below with your specific needs.
What’s inside a Compressor
Check for Recalls
- US Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) – Resource for Recalls
- GE Recall Central Site
- You can reach the GE Support at 1-800-626-2005. For parts, call 1-877-959-8688
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can you test the inverter?
- No, you cannot directly test the inverter without a specialized equipment not available to DIYer. You can only diagnose by verifying that the motherboard and compressor are in working order.
- What is the Liner Protection Mode?
- Applicable to GE refrigerators, the purpose of this feature is to start and run the evaporator fan on high sped if any door or drawer has been open for 3 minutes or longer.





Susan
Tuesday 30th of May 2023
we removed the divider from the top drawer of our GE bottom freezer.
The bottom drawer has one that clips on, but the smaller one seems to sit loose, but I'm sure it was in there tightly before.
I'd really appreciate it if you have something simple to pass on to me.
With thanks, Susan Willows